Introduction
Double materiality is an extension of the key accounting concept of materiality of financial information. It is a concept that has emerged in the context of sustainability-related financial disclosure.
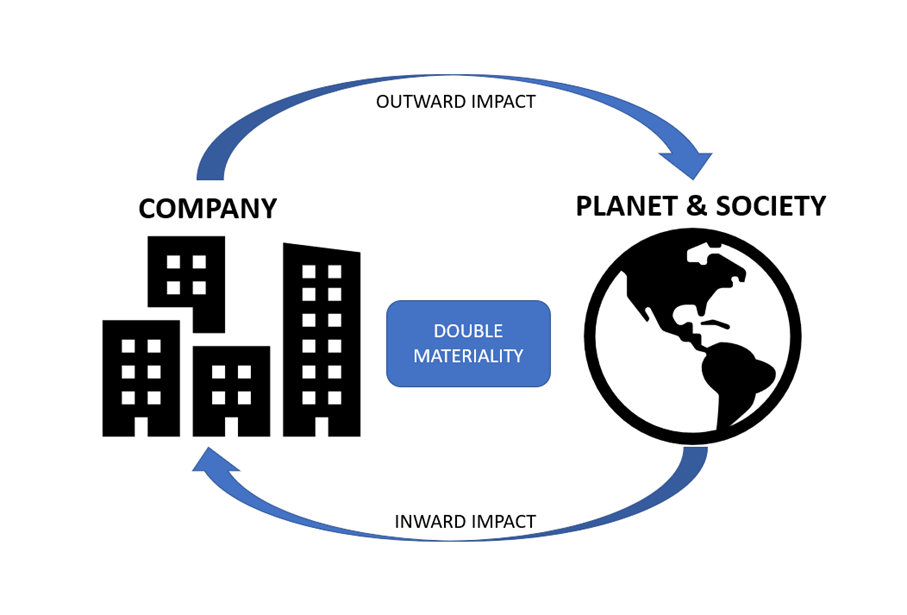
What is Double Materiality?
Double materiality is a concept that has gained prominence in the realm of sustainability reporting, particularly with the upcoming European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS).
This framework introduces a structured approach for determining the inclusion of sustainability topics or information in a company’s sustainability report.
It goes beyond the traditional concept of materiality in sustainability reporting by emphasizing the dual impact of sustainability issues on a company and the reciprocal impact of the company’s activities on society and the environment.
Key Aspects of Double Materiality
- Two Perspectives: Double materiality requires companies to consider two perspectives: What is material to them?
What is material to society or the planet?
2. Incorporating Environmental Impacts: It brings environmental impacts into the focus of standard-setting in accounting, extending the traditional concept of materiality to encompass the impacts of a company on the climate, environment, and society.
3. Regulatory Influence: The European Commission and the International Sustainability Standards Board have been instrumental in defining and incorporating double materiality into sustainability reporting guidelines, reflecting a global shift in reporting requirements.

Implications and Challenges
- Expanded Reporting Scope: The inclusion of double materiality as a mandatory requirement expands the scope of sustainability reporting, aligning with stakeholder expectations and influencing transparency and sustainability strategies of reporting companies.
- Data Gathering and Communication: Gathering and communicating a broad spectrum of data related to double materiality poses significant challenges for companies, requiring them to identify, assess, and report on their impacts on people, the environment, and society.
Moving Forward
As companies navigate the evolving landscape of sustainability reporting, understanding and integrating the concept of double materiality will be crucial. It not only fosters a more comprehensive understanding of a company’s role in a wider context but also aligns with the growing emphasis on transparency, stakeholder trust, and sustainable investment practices.
In conclusion, double materiality represents a pivotal shift in sustainability reporting, emphasizing the interconnectedness of a company’s operations with environmental and societal impacts. Embracing this concept can empower companies to enhance their sustainability strategies, meet regulatory requirements, and contribute to a more transparent and sustainable business environment.

