ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) risk management can be found in the dictionary under ‘S’ for sustainable. It requires being able to recognize, evaluate and take care of those risks that could influence a company’s environmental standing as well as its social responsibility and governance framework. At the center of this process is one important tool: the ESG risk matrix assessment. This tool sizes up possible risks based on their probability and potential impact levels before mapping them out on a matrix that helps in coming up with an action plan or deciding where more resources should be channeled.
There are many reasons why it is very important to manage ESG risks effectively. But to benefit from these risks, companies have to address them proactively; this way they can evade legal penalties, shield their image and ensure that they meet stakeholder expectations. In addition, the proper management of these risks leads to a long-term value creation which supports the sustainable development goals— ESG risk matrix should always be considered part of any strong ESG strategy as part of a full assessment.
What is ESG Risk Matrix Assessment?
The ESG risk matrix evaluation is a strategic weapon used to find, assess, and place value on the risks of environmental situations (the first ‘E’ in ESG), social and governance within an organization. The problem helps companies realize what could be an effect and how much it could be possible about different ESG risks; this allows them to spend money wisely on taking measures to prevent these risks.
The visual representation of the assessment is illustrated by plotting identified risks on a matrix which usually have two axes, one indicating the likelihood and the other showing the impact. This tool helps in prioritizing different risks according to their level of criticality.
There are primary elements that make up an ESG risk matrix:
- Identification: Efforts must be put into compiling an exhaustive list of potential ESG risks that hold relevance to the organization.
- Risk Probability: This refers to estimating the likelihood of each risk.
- Risk Severity: This involves determining the possible impact or seriousness of each risk.
- Risk Matrix Analysis: The risks are positioned on a matrix to decide which ones should be dealt with immediately.
- Action Plans for Risks: Strategies are planned and acted upon after prioritizing high risks.
By systematically assessing ESG risks via a risk matrix evaluation, companies can deal with unknowns more effectively— which also helps boost resilience (reducing such negative impacts) and sustainability.
Significance of ESG Risk Matrix Assessment
ESG risk matrix: An important tool in the identification and prioritization of risks, allowing organizations to direct their attention towards the most critical areas that can hamper their business and standing. By methodically assessing the probability and severity of different ESG risks, firms are empowered to make wise executive choices— channeling resources where they are most needed and engineering strong mitigation blueprints.
An evaluation contributes significantly to steering a clear course in strategic decision-making by establishing a systematic view of major risks related to ESG. The effect and impact of these risks will thus be instrumental in helping organizations merge their sustainability strategies with their mission-critical goals— an action that engenders a superior level of resilience and risk control.
In addition, a well designed ESG risk matrix evaluation can drive a company to take better care of the sustainability, which in its turn will help address risks in a more proactive way for environmental and societal harm or misgovernance. It fosters trust among stakeholders by showing — through the development of ESG issues with an open hand — dedication to transparency and accountability, thus winning stakeholder trust. The approach is being highly valued by various stakeholders such as investors, customers and regulators who appreciate companies taking proactive actions toward ESG risk management: it enhances reputation and can result into greater competitive advantage for the company.
Key Components of ESG Risk Matrix Assessment
Identification of Risks
To create an ESG risk matrix assessment, you must first find all the environmental, social, and governance risks (ESG) that can affect your organization. This is not only just an overview of the policies and procedures but also a detailed analysis of what lies within and outside their jurisdictional control including possible legal changes or any other laws, environmental happenings that might impact them socially as well numbers trends because those too come into play. The best way to gather information about these areas is through involving stakeholders who are involved in different aspects of the business as well as looking at industry benchmarks which can highlight common risk areas.
Assessment of Risk Likelihood and Impact
Once the risks have been identified, the next course of action is to assess their probability and effect level. This means determining how likely each risk is in reality to occur and what kind of damage it might cause if it does happen. Usually, this is achieved through a quantitative approach— risks are measured based on both their likelihood and impact using a numerical scale. This gives rise to an ordinal scale which has been proven mathematically sound: the combination of two numeric scales provides better ordinal data that one cannot obtain with qualitative methods only.
After risks have been assessed, the next move is to rank them according to their likelihood and impact scores. High-likelihood, high-impact risks take precedence because they are considered the most menacing towards the organization. The prioritization task allows for concentration of both resources and attention on those risks that are critical; thus ensuring that major threats are dealt with at the earliest stage.
Preparation for Action on Risk Mitigating Strategy
The last step is to come up with tactics that will help in reducing the risks that have been recognized and prioritized. It involves coming up with action plans which can either reduce the chances of the risk occurring or lessen its impact. Policy changes, process improvements, technology investments, or stakeholder engagement initiatives are examples of strategies that can be taken into consideration as mitigation strategies. An oversight on these actions makes certain their viability and applicability is maintained: Continuous monitoring and review of these strategies ensure they remain effective and relevant.
Here’s a simple diagram illustrating these components
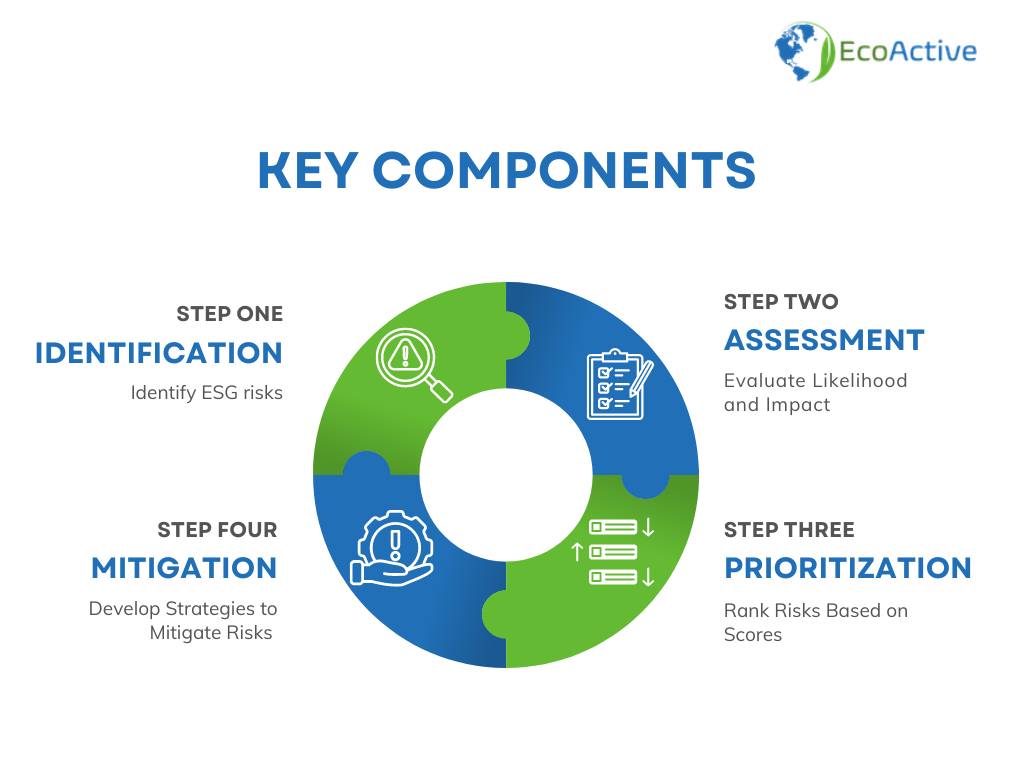
To have their ESG risks systematically identified, evaluated and managed which in turn can enhance the organization’s resilience and sustainability, this approach is proposed.
Best Practices for ESG Risk Management
Regular Update of the Risk Matrix
ESG risk matrix keeping current is very important. It would be via regular updates, in which new risks are identified and evaluated on time while the existing ones are re-assessed based on up-to-date information and trends. The dynamic nature of this approach enables organizations to proactively address emerging risks and evolve with changing situations.
Involvement of Cross-Functional Teams
Achieving this level of effective ESG risk management implies the contribution of different departments to an organization. When diverse perspectives and expertise converge through the synergy of cross-functional teams, the outcome is a more complete and holistic approach in identifying and assessing risks. It takes all: involving stakeholders from finance, operations, legal, sustainability and any other related area guarantees that every possible risk is taken into consideration and consequently managed with an iron fist.
Integration with Corporate Governance Frameworks
The entrenchment of ESG considerations within the core strategic and operational decision-making processes, through an integration of ESG risk management with corporate governance frameworks. This alignment fosters a sense of responsibility for ESG risks at the top tier of the organization — promoting accountability and oversight in decision-making processes.
Use of Advanced Analytical Tools and Technologies
The use of powerful analytical tools can greatly improve the precision and efficacy of ESG risk assessments. With such tools as predictive analytics, artificial intelligence and machine learning, it becomes easier to gain a more profound understanding of risk patterns and trends. These technologies facilitate the quick processing of huge amounts of data for organizations— allowing identification of correlations and prediction of risks on a larger scale with more precision.
Inculcating these best practices would enable firms to boost their ESG risk oversight capacities; a precursor to increased anti-fragility, stakeholder trust levels and, eventually, the sustenance of their operations over the long haul.
Challenges and Solutions in ESG Risk Matrix Assessment
Data Availability and Quality
The difficulty of gathering complete and precise ESG data arises from the inconsistency of reporting standards and the unavailability of reliable data sources. However, one way to surmount this challenge is by putting in place a sound data management system that obtains information from different points and integrates them together then conducts regular audits as well as validation processes to ascertain its accuracy.
Complexity of Risk Assessment
Measuring ESG risks can be quite a challenging task given that these risks are interdependent and involve complex relationships. It is not easy, but understanding the organization enough is to be aware of different factors affecting it. Adoption of high-level analytical tools like artificial intelligence and machine learning makes it possible to analyze large data sets effectively by easily identifying patterns, correlations, and risks.
Engaging Stakeholders
To effectively involve a wide range of parties, an entity with all the necessary contributions could be complex and time-consuming. However, it can be achieved through this process: Develop organized stakeholder engagement procedures (which may include surveys, interviews or workshops) and ensure open channels of communication. This will bring in complete feedback and let stakeholders know what is happening so that they can participate in the risk assessment process.
Prioritizing Risks
Identification and prioritization of material issues from a wide range of ESG topics may seem like an insurmountable task. However, applying materiality matrices along with industry benchmarks to methodically evaluate and assign priorities based on the significance and impact value to stakeholders can help streamline this process. It is also essential to keep track of the prioritization at regular intervals; making updates in accordance to changes noted within the business environment.
Integration with Corporate Strategy
It is not always easy to align the identified material issues with the core business strategy. A close collaboration between the sustainability and strategy teams (ensuring cross-functionality) is one way of embedding materiality findings into strategic planning. This also includes developing clear action plans that see ESG considerations as part of the performance metrics towards business objectives and, thus, helps in making sure these two are aligned.
Practical Solutions and Tools
- Data Analytics at its Best: Employ predictive analytics and machine learning to boost the precision level of risk detection and assessment.
- Platforms for Stakeholder Collaboration: Introduce digital platforms that will allow stakeholders to engage easily with your company’s operations on a continuous basis as well as provide feedback promptly.
- Reporting Tools That Tell the Whole Story: Opt for software that marries ESG risk management with financial and operational reporting systems— thus making two processes one, while enhancing the quality of data through consistency.
- Training and Capacity Building: Staff should be trained frequently on ESG risk assessment techniques, including how to get data properly and why it is important to report accurately.
- External Consultancy: Establish connections with experts in the field of ESG who can provide you with useful information regarding best practices in managing ESG risks.
In this way, businesses can tackle these challenges head-on with practical approaches and resources that will help boost their ESG risk matrix evaluations. And a better risk management isn’t just for show: it nurtures stakeholder trust, which fosters corporate sustainability performance.
Conclusion
The ESG risk matrix assessment is essential in recognizing, prioritizing, and controlling environmental, social, and governance risks. Through a structured approach to these risks, companies can improve transparency (seeing through the situation clearly), demonstrate stakeholder trustworthiness (showing that stakeholders can rely on them), and operationalize sustainable performance. On an ESG risk management basis: it is worth considering best practices which would include updates that are regular and achieved through cross-functional collaboration plus addressing challenges commonly identified with advanced tools and process flows. As more organizations seek to weave ESG threads into the fabric of their strategic plans: use of this risk matrix will be pivotal not only in building resilience but also in supporting sustainability efforts— be sure to toss aside those formulaic approaches when creating or evaluating such assessments!
The adoption of the ESG risk matrix assessments is highly recommended for businesses to improve their sustainability practices and better manage risks. EcoActive ESG provides such an all-encompassing tool— from sophisticated analytical solutions, through stakeholder engagement frameworks up to strategic planning support. With EcoActive ESG, organizations can rationalize their ESG risk management processes that can be more closely aligned with their primary business goals. For personalized advice or more information on how the journey of sustainability can be supported by EcoActive ESG, contact our team of specialists today.



