In today’s rapidly evolving regulatory and investment landscape, Integrated Financial and ESG Reporting is no longer a “nice-to-have”—it is becoming a global standard.
This shift is being driven not only by compliance requirements but also by the growing demand from investors, regulators, and stakeholders for transparency, accountability, and long-term value creation. In fact, 90% of S&P 500 companies now release ESG reports, with many highlighting how climate change impacts their operations and strategies. But ESG reports published in isolation often fall short—they need to be connected to financial outcomes to provide the “full picture” of corporate performance.
For investors, integrated reporting provides greater transparency, comparability, and confidence in decision-making. Organizations that embed ESG metrics seamlessly into their financial reporting will not only stay ahead of regulatory scrutiny but also gain a competitive edge by signaling credibility, resilience, and future-readiness to the market.
Why Independent ESG Reporting Falls Short
For years, ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) reporting lived in a silo, typically presented in glossy sustainability reports. While they signaled corporate responsibility, these standalone documents also created challenges:
- High Costs & Duplication – Companies produced separate ESG and financial reports, duplicating effort and increasing compliance costs.
- Fragmented Information – Sustainability metrics rarely aligned with financial data, making it difficult for stakeholders to understand the real impact of ESG initiatives.
- Lack of Comparability – With multiple voluntary frameworks (GRI, SASB, TCFD), disclosures lacked consistency, fueling skepticism about credibility.
- Regulatory Pressure – Voluntary reporting is no longer sufficient—mandatory integrated disclosures are fast becoming the global norm.
- Risk & Financial Blind Spots – Keeping ESG and financial disclosures separate often masks the connection between sustainability risks (like climate change, supply chain disruptions, or social issues) and their financial implications. This disconnect limits investor insight and leaves companies exposed to hidden vulnerabilities.
Simply put, separate ESG reports are outdated in today’s interconnected business world.
What is Integrated Reporting?
Integrated reporting combines financial performance metrics and sustainability disclosures (ESG data) into a single, comprehensive report.
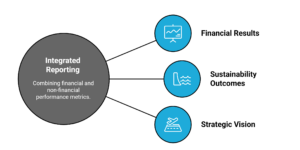
It brings together:
- Financial results – revenue, profitability, and shareholder returns.
- Sustainability outcomes – climate impacts, governance structures, diversity, and supply chain performance.
- Strategic vision – how the company will grow while managing ESG risks and creating future value.
Think of it as the “full picture” of a business. Instead of looking at profit in isolation, integrated reporting explains how profit was achieved and at what cost — or benefit — to society and the environment.
The Shift: From Voluntary to Mandatory Integrated Reporting
The move toward Integrated Financial and ESG Reporting is being fueled by regulatory momentum worldwide:
- European Union (EU): The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), developed by the EU through EFRAG, marks a major step in advancing corporate transparency. Taking effect from 2023–2024, it requires companies to include detailed sustainability information within their management reports, structured in line with the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS). To ensure accessibility and comparability, these disclosures must also be digitally tagged in XBRL under the European Single Electronic Format (ESEF) framework.
- United Kingdom (UK): The Financial Reporting Council (FRC) mandates climate-related disclosures aligned with the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), embedding ESG directly into financial reporting.
- California’s Climate Law: California’s Climate Accountability Package, which includes SB 253 (Climate Corporate Data Accountability Act) and SB 261 (Climate-Related Financial Risk Act), will require large companies doing business in the state to disclose Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions as well as conduct climate-related financial risk assessments.
- Global Standards (ISSB & IFRS): The International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB), operating under IFRS, is developing a unified baseline for sustainability disclosures, ensuring that ESG data is financially material and globally comparable.
The message is clear: the era of voluntary ESG reporting is over. Businesses must integrate financial and sustainability disclosures to remain compliant and credible.
Why Integrated Reporting Matters in 2025
- Stronger Compliance Alignment
With frameworks like CSRD and ESRS in the EU, ISSB standards globally, and TCFD-aligned disclosures, integrated reporting helps companies stay aligned with evolving regulations.
Unified reporting avoids the risks of fragmented submissions across multiple regulators. - Improved Data Consistency
When finance and ESG data are reported separately, inconsistencies often creep in. Integrated reporting ensures numbers reconcile across financial statements and sustainability disclosures. - Efficiency & Reduced Workload
By eliminating duplication between finance and ESG teams, companies can cut down reporting cycles, reduce manual errors, and streamline workflows. - Investor-Ready Transparency
Investors are increasingly screening companies on both financial returns and ESG credibility. Integrated reporting presents a coherent narrative, boosting market confidence. - Holistic Risk & Financial Disclosure
Integrated reporting links sustainability risks—such as climate exposure, resource dependency, or governance failures—directly with financial performance. This provides stakeholders with a clearer view of long-term value creation, resilience, and potential vulnerabilities. - Future-Proofing
Integrated reporting prepares organizations for the inevitable shift toward real-time, digital-first reporting ecosystems, where data accuracy, comparability, and transparency will define leadership.
Implementation Road map: How to Get Started
Adopting integrated reporting requires more than compliance—it’s about strengthening decision-making and transparency. Companies can move forward through these steps:
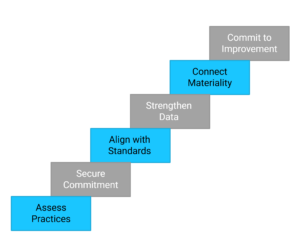
- Assess Current Reporting Practices
Review existing financial and sustainability disclosures to identify overlaps, gaps, and risk areas. This helps highlight where ESG issues connect with financial outcomes. - Secure Leadership Commitment
Integrated reporting succeeds when boards and executives sponsor the initiative, ensuring risk, finance, and sustainability functions work together. - Align with Standards and Regulations
Select frameworks relevant to your market—CSRD, SEC climate disclosures, ISSB, or GRI—and map how they impact both financial and non-financial reporting. - Strengthen Data and Technology
Establish a structured system for collecting, validating, and storing ESG data alongside financial metrics. A digital-first approach ensures disclosures are accurate, comparable, and audit-ready. - Connect Materiality with Risk Management
Prioritize ESG issues that have direct financial relevance or present long-term risks, integrating them into corporate strategy and reporting narratives. - Commit to Continuous Improvement
Integrated reporting is an evolving journey. Each cycle should enhance data quality, risk transparency, assurance practices, and the clarity of financial-ESG linkages
How EcoActive Transforms Integrated Reporting
EcoActive is more than a compliance tool — it’s a comprehensive platform designed to make integrated reporting seamless, intelligent, and future-ready. By unifying financial disclosures and ESG performance, EcoActive empowers organizations to meet global requirements while building trust with investors, regulators, and stakeholders.
Key Capabilities That Set EcoActive Apart
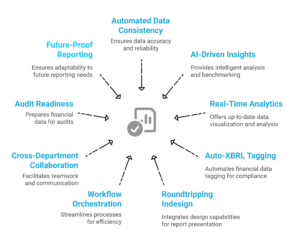
- Automated Data Consistency
Our platform provides data consistencies, running automated checks for accuracy and alignment. This reduces the risk of discrepancies and ensures audit-ready outputs every time.
- AI-Driven Insights & Benchmarking
EcoActive uses advanced AI to generate predictive insights, peer benchmarking, and trend analysis, helping companies move beyond reporting to strategy-building.
- Real-Time Analytics & Dashboards
With interactive dashboards and real-time monitoring, decision-makers gain a clear, consolidated view of financial and non-financial performance — all in one place.
- Auto-XBRL Tagging & Validation
Our automated XBRL tagging and validation engine ensures that every report meets regulatory technical requirements — cutting manual effort, time, and errors.
- Roundtripping Indesign capabilities
EcoActive’s Roundtripping InDesign capability enables smooth back-and-forth between structured ESG/financial data and professionally designed report layouts, with XBRL tagging fully retained throughout the process. This ensures compliance accuracy, eliminates manual rework, and delivers investor-ready, publication-quality reports seamlessly.
- End-to-End Workflow Orchestration
From data collection and validation to narrative drafting and final submission, EcoActive supports the full lifecycle of integrated reporting with transparency and efficiency.
- Cross-Department Collaboration
EcoActive bridges finance, compliance, sustainability, and investor relations teams to establish a single source of truth for all disclosures.
- Audit & Assurance Readiness
Built-in validation frameworks ensure reports are reliable, transparent, and regulator-approved on first submission.
- Future-Proof Reporting
We prepare organizations for what’s next — Scope 3 emissions, supply chain transparency, and AI-led predictive disclosure standards.
The Future of Integrated Reporting
The next 3–5 years will see a reporting shift from annual filings to real-time, connected data ecosystems. Organizations can expect:
- AI-driven analysis that converts reporting into actionable strategy.
- Global alignment of ESG frameworks, reducing duplication.
- Mandatory disclosures on biodiversity, social equity, and governance integrity alongside financials.
Those who embrace integrated reporting today will be better positioned to adapt tomorrow, earning stronger investor trust and competitive differentiation.
FAQs on Integrated Reporting
Q1. Is integrated reporting mandatory?
Yes, in many jurisdictions — particularly the EU under CSRD. In other regions, it’s becoming an investor expectation even if not yet a legal requirement.
Q2. What’s the biggest benefit of integrated reporting?
It provides a clear, consistent, and credible narrative by connecting financial results with sustainability impacts, boosting both compliance and trust.
Q3. How do companies start preparing?
By aligning internal processes, ensuring data quality, and adopting recognized reporting frameworks with guidance from experts like EcoActive.
Conclusion
The reporting landscape is evolving rapidly. Financial reporting alone doesn’t capture the risks and opportunities of today’s world. ESG reporting in isolation doesn’t explain long-term value creation. Integrated reporting brings both together.
At EcoActive, we help organizations navigate this shift with confidence — ensuring that disclosures are not just compliant, but comprehensive, credible, and future-ready.
👉 Ready to strengthen your integrated reporting approach? Get in touch with EcoActive.



